Europeans collected a huge number of Aboriginal artefacts during the colonisation of Australia. These include weapons, bags, toys, clothing, canoes, tools, ceremonial items, and ancestral human remains. Many institutions that hold these items are repatriating them to Aboriginal people. While repatriation is important, what often goes unrecognised is the crucial part that collectors played in the violent of First Nations people.
My research is on the ’s collecting networks. Formed in 1862, the museum amassed a significant collection of Aboriginal artefacts over the following 60 years. Despite countless, undocumented interactions between makers, owners, collectors and curators, many of which were no doubt benevolent, frontier violence was a crucial aspect of the museum’s collecting.
Instances of grave robbing and body snatching as methods of are not to Queensland. Many institutions in Australia and abroad have problematic acquisition histories, particularly in relation to the study of .
Activists have been agitating for the return of cultural materials for decades, and museums across Australia, including the , have programs and policies. It works closely with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities to prioritise the return of ancestral remains and sacred objects. But much material collected through violent means is still held in its collection.
While there is no evidence of the museum being directly involved in frontier killings, the use of the police, protectors, missionaries and frontier doctors as the dominant network of collectors implicates the museum as a passive beneficiary of dispossession.
In a response to The Conversation, the Queensland Museum said: “We believe these are important stories to be told and understood, and we recognise past hurts and are actively working to address these issues.
"Queensland Museum Network acknowledges that between the 1870s and 1970s, a number of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Ancestral Remains, Burial Goods and Secret and/or Sacred Objects were acquired without consent or due regard to traditional lore and custom.” Illustration of the new Exhibition Building at Bowen Park, 1891. State Library of Queensland
Illustration of the new Exhibition Building at Bowen Park, 1891. State Library of Queensland

Dispossessing and collecting
In the 1870s, police Sub-Inspector , noted for his role in of Aboriginal people, sent the Queensland Museum ancestral remains and burial goods. These had been stolen during punitive raids on Aboriginal people in the Gulf of Carpentaria.
The following decade, Francis Lyons, a “”, offered the museum mummified remains he had stolen during a retributive attack on Aboriginal people. In his accompanying correspondence he wrote:
They abandoned everything except the [remains] … and it was not until after a long and desperate chase, and when their lives were in imminent danger that the[y] … dropped it.
In many instances cultural items – mostly weapons and bags – were purchased from Aboriginal people. The museum issued its collectors with tobacco for payment, itself pointing to the power imbalance of frontier currency. Yet as both Lyons and Douglas’s cases show, items were also removed after Aboriginal people were forcibly dispossessed from their country, taken from the surface, and at times stolen following raids.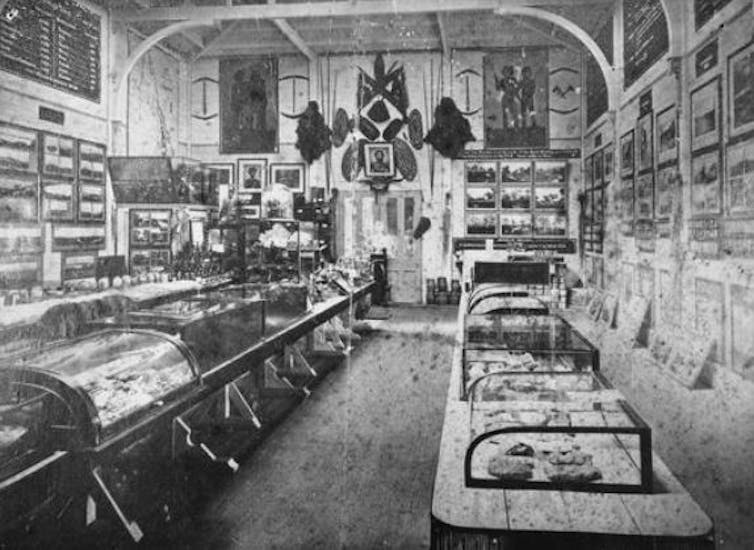 Inside Queensland’s first natural history museum, 1872, showing Aboriginal artefacts and images on the back wall. State Library of Queensland
Inside Queensland’s first natural history museum, 1872, showing Aboriginal artefacts and images on the back wall. State Library of Queensland

Some ancestral remains held by the museum were . Remains were dug up, stolen from caves, burial trees, and bags, depending on regional customs.
While these practices may have sat outside the bounds of European expectations of death and burial, the plunderers were acutely aware of the damage they were inflicting. One correspondent informed the museum in 1880 that exhuming the remains of a recently deceased man was “too much like desecrating unless it was in the interest of science”. The idea of contributing to scientific knowledge was used to justify these actions.
Remains were also plundered from massacre sites, often decades after the event, as well as former mission sites, and sent to the museum with the sanctioning of the police and protectors.
Remains were also taken from regional hospitals, at times with the approval of the , the government agent responsible for Aboriginal people. Rogue doctors stole others from post-mortem rooms. In 1885, for example, the remains of labourers were sent from the Polynesian hospital in Mackay with specific instructions to “make them look a little ancient”.
Empire and science
The emergence of in the mid-19th century, combined with the British Empire’s expansion, drove the desire for Aboriginal artefacts. Objects were collected as anything from to scientific specimens, tendentiously used to “prove” European superiority.
With an interest in the “science of man”, the Queensland Museum’s curatorial staff maintained a network of collectors across the colony through relationships forged with (predominantly) men in remote locations. They included missionaries, journalists, station managers, doctors and public servants. A 1911 targeted these networks, stating that “every effort” must be made in “acquiring those symbols of the life of the original Australian inhabitants whose rites, ceremonies, customs and traditions are becoming obsolete and being entirely lost to us”. Plate from The Evolution of Culture, Augustus Henry Lane-Fox Pitt-Rivers, 1906, Plate XII.
Plate from The Evolution of Culture, Augustus Henry Lane-Fox Pitt-Rivers, 1906, Plate XII.

However, the most profitable collectors were the government agents regulating Aboriginal people’s lives. For example, from the 1870s, the police channelled material and information to the museum. The became particularly important contributors.
The museum exploited their violent methods of colonial policing and – a euphemism for massacre – and the police themselves noted this role. Following his dismissal from the force, and five years after leading an attack on Aborignal people at Creen Creek, former Native Police officer William Armit of ethnographic collecting that “no one can be more fortunately situated for such work than the Native Police officers”.
The passing of the Aboriginal Protection and Restriction of the Sale of Opium Act also led to increases in the museum’s acquisitions. Protectors, such as Northern and later Chief Protector and Southern Protector , were active collectors. They became two of the museum’s largest donors with upwards of 700 items between them, both acquiring material through their official duties.
Collecting as violence
Apart from benefiting from the spoils of colonial violence, the act of collecting itself can be seen as violent. – the social, cultural, legal, economic and political structures that marginalise groups – does not only cause physical harm, it also inflicts damage on the mind and spirit.
Collectors knew that taking ancestral remains from burial places would cause harm. Indeed one collector noted: “I feel repugnance to hurt their feelings willingly.” While procurement may have been void of direct violence, waiting for an old man to die in order to send his body to the museum, as in one case in 1915, was a malevolent act of indirect violence.
Taking materials from country also served Europeans in claiming possession, both emotional and physical, of the land. By removing Aboriginal people and culture, the invaders were writing their own narratives of ownership over the land. As were built on the dispossession of Indigenous people, the removal of cultural materials became part of the appropriation of land.
While repatriating Aboriginal cultural materials is undeniably important, we must also acknowledge the histories behind their collection. This is an important part of the repatriation process itself.
Gemmia Burden does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.









