When the battered body of 25-year-old was found in Royal Park in Melbourne on Saturday, 25 May, it was not the first time a homeless person had been killed in Melbourne.
But, as with then 2012, this particular case has shocked the community and, according to informed sources, rattled the Victorian government.
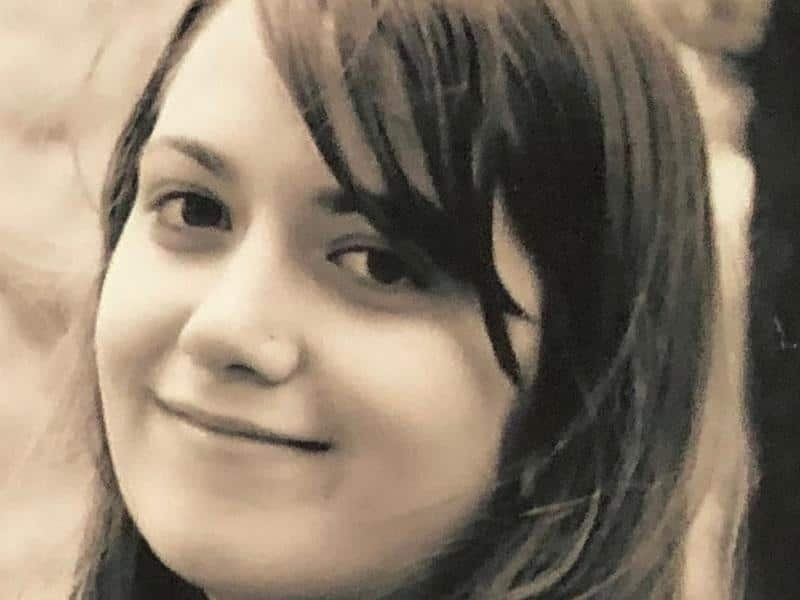

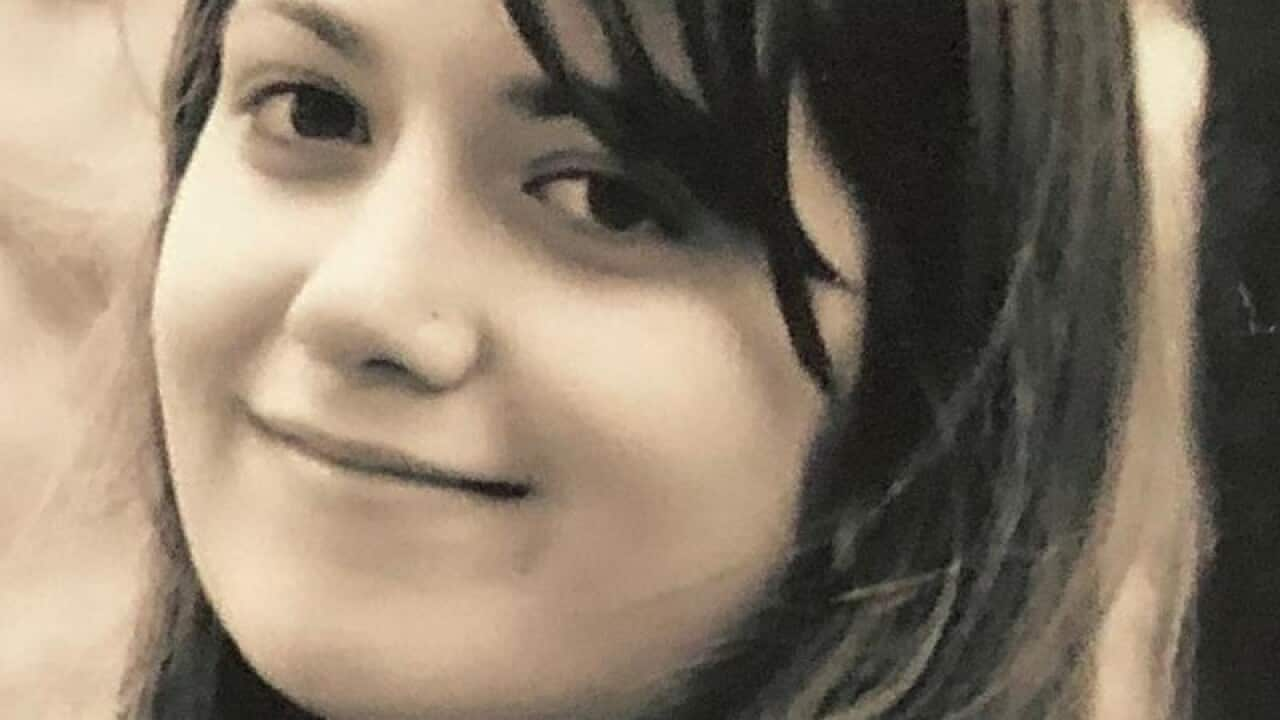
Courtney Herron, 25, was found bashed to death in an inner-city Melbourne park. Source: Supplied
. She was experiencing mental health issues and trying to deal with drug addiction. Her shocking death, an act of violence against a young woman, reminds us of the vulnerability of rough sleeping, and the disturbing and continuing reality of youth homelessness.
Some advocates are calling for a renewed focus on rough sleeping and more crisis accommodation in the major cities where homeless people are most visible. Such advocacy is well-intentioned but deeply misguided.
We need sustained housing strategies, not quick fixes
Similar proposals have been raised before. In the early 1990s, there were calls for the empty 11-storey Prince Henry Hospital complex on St Kilda Road to be turned into a shelter for the homeless.

Mourners gather for the vigil for Courtney Herron, at Royal Park in Melbourne. Source: AAP
The spectre of a new generation of homelessness shelters haunted a city in which the dormitory shelters such as “The Gill” had only recently been decommissioned. Fortunately, experienced social workers came forward to advise Melbourne City Council not to bow to loud but misguided advocacy. The proposed Prince Henry Shelter complex did not happen and the hospital was demolished in 1994.

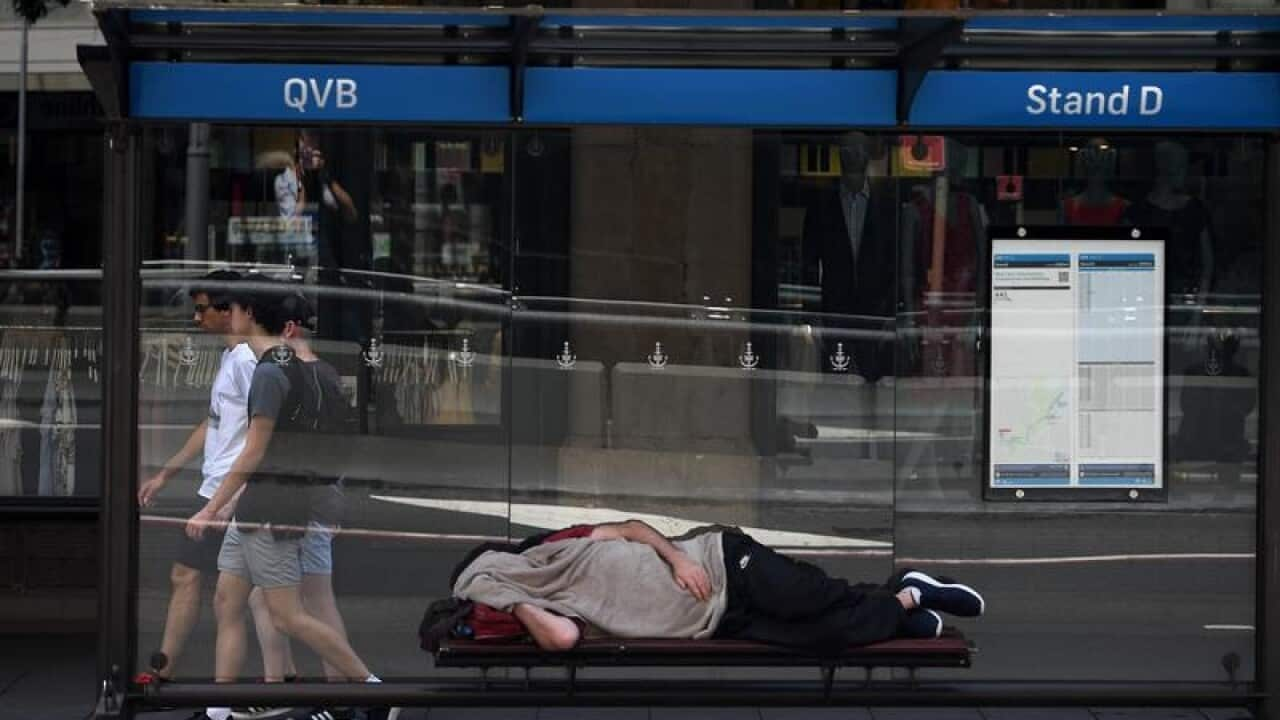
A man sleeping in a bus shelter outside the Queen Victoria Building in Sydney. Source: AAP
Of course, there needs to be an efficient and effective response to rough sleeping in the Melbourne CBD and in . Only last year Victoria’s Homelessness and Rough Sleeping Action Plan was launched, backed by a A$9.8 million Towards Home package, “to provide housing and support to an increasing number of people sleeping rough across inner Melbourne”.
The fact is that the goal of housing rough sleepers has not been achieved, despite many attempts over the years. Could it be that a knee-jerk symptomatic response from government, which so often falls short of strategic action, is part of the problem?
Developing more crisis accommodation seems to make common sense, which is probably why such proposals continue to be raised. Crisis accommodation supports people who are currently homeless. It has an immediate and short-term impact, but cannot reduce homelessness.
So what needs to be done?
If we are seriously to reduce homelessness in a sustained way, counterintuitive thinking and action are required, not simplistic “common sense”.
Pouring more public funds into crisis accommodation simply treats the symptoms of the problem. But it does not contribute to a reformed service system that can begin to make serious inroads into reducing the problem. According to the National Report Card on , issued in March 2019, two of the four key policy imperatives are:
- to stem the flow of young people into homelessness or early intervention
- to get young people out of homelessness as quickly as possible by providing rapid rehousing options and an accessible and affordable youth housing sector for young people who have become homeless and have nowhere to return to.
The current service system is mostly a crisis response. Early intervention capacity is grossly underdeveloped and youth housing options are limited.

In general, we don’t need more crisis services, but we do need much greater early intervention and youth housing capacity.
While we don’t know the detailed circumstances of how Courtney Herron came to be sleeping rough, there would have been many opportunities to avert her descent into homelessness. But, even if that were not practicable, she should never have been left to sleep out in Royal Park. The sad, most likely scenario is that her death will not bring on strategic reform but only more short-term crisis responses and a push to get more homeless people off the streets quickly.
On the other hand, this tragic death could be a catalyst for real change. We need to do much more. More to the point, we could and should do so much better.
Associate Professor David MacKenzie has received funding from the ARC, philanthropic foundations and various Australian governments. He is Chair with the charitable NGO Youth Development Australia Ltd (YDA), which is the auspice for the National Youth Commission on Youth Employment and Transition (NYC) and also Chair of My Foundations Youth Housing Co. David was part of the team that wrote the 2019 National Report Card on Youth Homelessness 2008-2018.
Dr Tammy Hand currently receives funding from various Australian governments and the AHURI. Tammy is affiliated with the NGO Youth Development Australia Ltd (YDA), which is the auspice for the National Youth Commission on Youth Employment and Transition (NYC). Tammy was part of the small team that undertook the assessments and wrote the 2019 National Report Card on Youth Homelessness 2008-2018.










