Key points
- The world is expected to grow to 8 billion people on Tuesday, three times higher than in 1950.
- The global growth rate could fall to around 0.5 per cent by 2050 due to a decline in fertility rates.
- The UN projects the population to peak at around 10.4 billion in the 2080s before starting to decline.
The world is expected to grow to 8 billion people on Tuesday, more than three times higher than the 2.5 billion global headcount in 1950.
And our global population will continue to grow, albeit at a slower pace and with regional disparities, in the decades to come — until it eventually starts to decline.
Here are the key takeaways, according to UN analysis.

The global population is more than three times higher than the 2.5 billion global headcount in 1950 and it will continue to grow before peaking and then steadily declining. Source: SBS News
Population growth is slowing
The world's population growth rate peaked in the early 1960s and since then has decelerated dramatically, Rachel Snow of the UN Population Fund told AFP.
Annual growth has fallen from a high of 2.1 per cent between 1962 and 1965 to below 1 per cent in 2020.
That figure could potentially fall to around 0.5 per cent by 2050 due to a continued decline in fertility rates, the United Nations projects.

The population growth rate of Australia and the world is steadily decelerating due to declining fertility rates. Source: SBS News
We will peak this century
Given the increase in life expectancy as well as the number of people of childbearing age, the UN projects the population to continue growing to about 8.5 billion in 2030, 9.7 billion in 2050, and a peak of about 10.4 billion in the 2080s.
Other groups have, however, calculated different figures.
The US-based Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) estimated in a 2020 study that the global population would max out by 2064, without ever reaching 10 billion, and decline to 8.8 billion by 2100.
"We are lower than them (the UN) and I think we have a good reason," lead author of the IHME study, Stein Emil Vollset, told AFP.
The University of Washington professor says that under their "quite different fertility model", the human population will only reach somewhere between nine and 10 billion.
Fertility rates are dropping
In 2021, the average fertility rate was 2.3 children per woman over her lifetime, down from about five in 1950, according to the UN, which projects that number to fall to 2.1 by 2050.
"We've reached a stage in the world where the majority of countries and the majority of people in this world are living in a country that is below replacement fertility," or roughly 2.1 children per woman, Ms Snow says.

Global fertility rates are gradually dipping, which means eventually our population will decline too. Source: SBS News
Life expectancy is rising and the population is greying
A key factor driving global population growth is that average life expectancy continues to increase. It was 72.8 years in 2019, nine years more than in 1990.
The UN predicts an average life expectancy of 77.2 years by 2050.
The result, combined with the decline in fertility, is that the proportion of people over 65 is expected to rise from 10 per cent in 2022 to 16 per cent in 2050.
This global greying will have an impact on labour markets and national pension systems, while requiring much more elderly care.
Ms Snow says that a growing number of countries are reaching out to her organisation, asking "how can UNFPA help us better understand what we might do to boost our population".
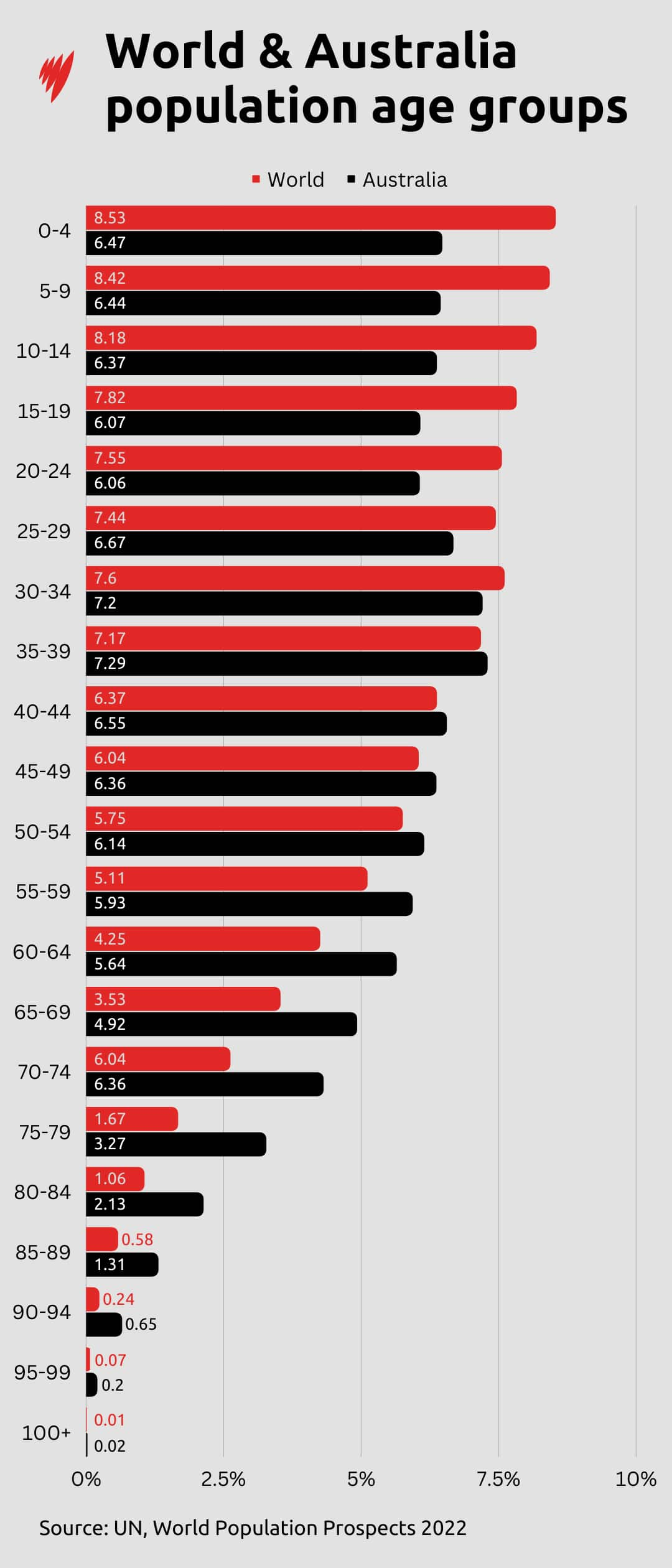
The global proportion of people over 65 is expected to rise from 10 per cent in 2022 to 16 per cent in 2050. Source: SBS News
There is unprecedented diversity
Beneath the global averages are some major regional disparities.
For example, the UN projects that more than half of the population growth by 2050 will come from just eight countries: Democratic Republic of Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines and Tanzania.
The average age in different regions is also meaningful, currently at 41.7 years in Europe versus 17.6 years in Sub-Saharan Africa, according to Ms Snow, who says the gap "has never been as large as it is today".
Those numbers could even out, but unlike in the past when countries' average ages were mostly young, says Ms Snow, "in the future, we may be closer in age, mostly old".
Some experts believe these regional demographic differences may play a significant role in geopolitics going forward.
India to surpass China
In another illustration of changing trends, the two most populous countries, China and India, will trade places on the podium as early as 2023, according to the UN.
China's 1.4 billion population will eventually begin to decline, falling to 1.3 billion by 2050, the UN projects.
By the end of the century, the Chinese population could fall to only 800 million.
India's population, currently just below that of China, is expected to surpass its northern neighbour in 2023, and grow to 1.7 billion by 2050 — though its fertility rate has already fallen below replacement level.
The United States will remain the third most populous country in 2050, the UN projects, but it will be tied with Nigeria at 375 million.
Australia's current population is 26 million.









